BIM
Building process management system from design to execution of works
The Building Information Modeling (BIM) is the perspective change that is spreading around the design&construction world in recent years, even in Italy. With BIM process, the construction&design planning, execution and management takes place on a methodological approach relied on different dimensions. This way, the design and construction process is made perfectly connected in the related context, integrated mode configured, real time modifiable and time-cost manageable.
The process relies on a parametric modeling technology, which can process and represent the dynamic behavior of the building.
The BIM role in construction industry is to support communication, cooperation, simulation and general improvement of building work lifecycle, managing information throughout design and construction phases up to the final maintenance phase.
BIM is a method for generating and managing information about buildings throughout their life cycle, from design and construction to management.
BIM process
BIM Method
The BIM method applies a “top-down” approach, allowing to create intelligent digital model of buildings, simulating and maintaining the same relations of the real one. The “top-down” approach starts with the 3D project visualization, enriched by further 4D, 5D and 6D visualizations. With this multidimensional representation it is possible to obtain also the traditional construction and project documents.
Relying on the ICT power, there has been in recent years the evolution of the building process .The typical linear process is evolving into the ‘cycle-to-cycle’ type, which provides intermediate evaluation and feedback throughout activities development.
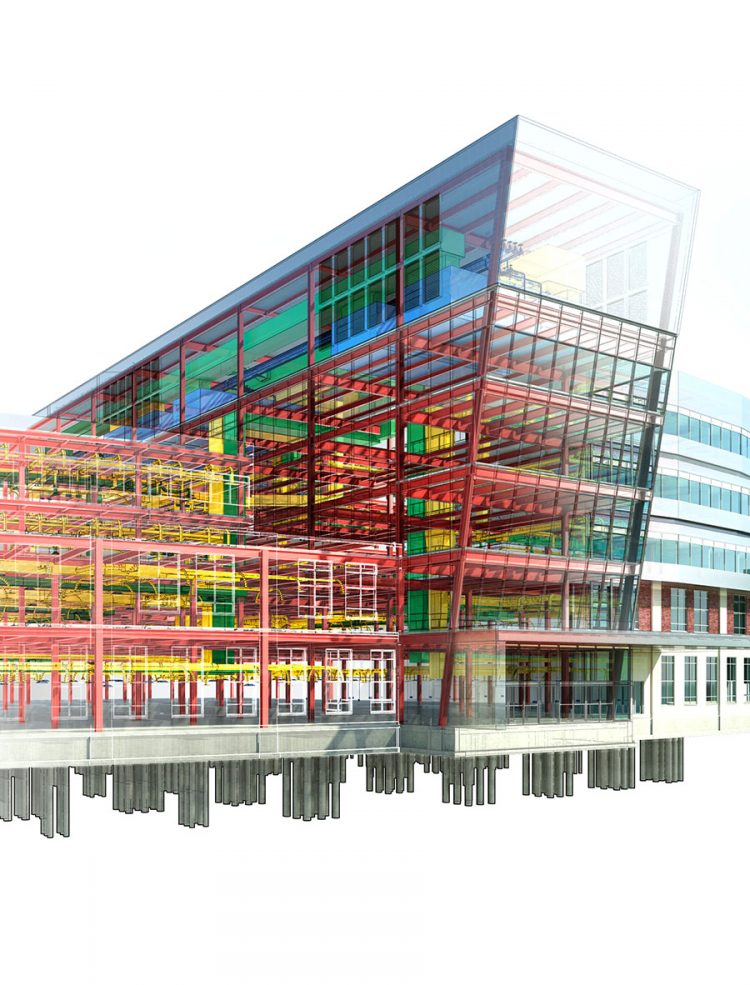


Parametric Model
The BIM model is a parametric model which contains project geometry as well as all technical, scientific, commercial and shopping information for a virtual representation of the planned works. The ability to change at any time this information, makes the dynamic model easy for data extrapolation useful to project documentation. The parameters are the contact point and the common language between the designer and the software. Simulating the real “behavior” of the elements that compose the project and highlighting any errors, clashes or inconsistencies, significantly reduce the number of “unexpected hazard” onto project and construction process.
Multidimensional Model
The BIM model is called multidimensional. Starting from the 3D size, it is able to represent the building up to 6 dimensions, in each of which are data content gradually increasing:
- 4D – in this size timing data have been inserted. Eg. once realized the Gantt chart and defined a reference date, you can visualize the 3D model with highlighted objects created or under construction
- 5D – in this size parametric cost estimate have been inserted. It is possible to view cost and project revenues curves and generate views of Budget through WBS
- 6D – in the size related to maintenance management, personal , functional, and related building techniques data are recorded to be useful for preventive maintenance
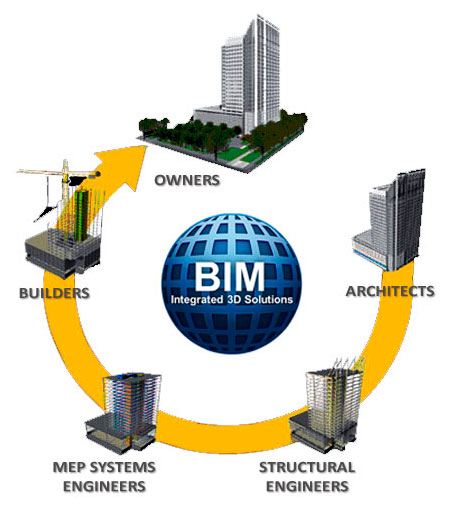
Building process
Through the BIM methodology, the whole building process is characterized by a constant two-way communication between the various figures involved:
- Client: use the model to optimize the efficiency of the building during its lifecycle, monitoring simply its maintenance
- Designer (architect, structural engineer and plant engineer): can quickly compare different conceptual alternatives, speeding up the information exchange and optimizing the design process
- Construction companies: they can use the model to simulate the construction work phases, checking out the work in progress, the timing and the cost trend
- Project manager: use the model for technical and economical monitoring
- Safety coordination: use the BIM model to define the onsite activities sequence and to have updated knowledge of operating working conditions and related dangers

Working Phases
Simulating the actual building construction, the BIM process manages the building work in progress, complying with a specific workflow:
- Step 1 – The first step is the definition of spatial references within which will develop the project. The positions in space of the virtual construction elements are established (for example pillars)
- Step 2 – In this phase are placed virtual building elements such as walls, floors, roofs, etc.
- Step 3 – Are inserted into the model openings such as doors, windows, curtain walls. Then it switches to the insertion of the vertical elements such as stairs, etc. until the completion of the building
- Step 4 – in this phase is prepared the project documentation that allows you to describe the work with interlocutors of the construction process, such as client, administration, stakeholders. New views are created, in addition to those of the base used for the model, to achieve the optimum artifact description.
Planning and Control
Relying on the knowledge of operations who must be completed on schedule for each constructive element, is possible to develop the work program knowing better the building dynamics involved. It is possible to create effective graphic simulations of the work in progress. Collaborating and working on the same model, it eludes errors due to inconsistencies between the various specialized disciplines, updating the model in real time, sharing through the cloud the design model, avoiding the information exchange slowness and simplifying the executive decisions.
Through careful cost analysis and resources usage it will come to a strict cost control and profit margins.
The BIM approach speeds up the economic computation processes. In effect for design review, the quantity takeoff is automatically updated with the new measures and simultaneously determines the value of each element of the project and then of the entire work.

BIM benefits
Even before the construction site has started, relying on BIM modeling it is possible:
- To check out the effects of construction on the related environment
- To perform simulations on the building energy performance
- To Check out interferences (for example, plants with structures)
- To greater speed up the documents creation
- To archive project documentation into a centralized database
- To ensure better final result in terms of quality, execution time, production and maintenance costs
The absolute advantage is:
- To update the project in real time
- To easily and quickly manage as-built documentation
- To reduce the inconsistency risk onto design drawings
- To reduce risks and unforeseen events during construction
- To communicate and collaborate, without loss of quality, with colleagues who deal with other sectors
- To integrate all stages of the building process
- To manage all the entire project information in an effective and coordinated way
Main Statistics
Based on studies of various construction projects implemented with BIM, the following trends have been detected:
- Design time: up to 7% discount on design time
- Time execution: up to 30% reduction in working schedules, relying on changes in progress time reduction
- Estimates spending time: up to 80% reduction in the time required to generate a cost estimate
- Variants: up to 40% less of unforeseen variations
- Cost: as the project is being deepened from the preliminary stage to the final, it is estimated that the accuracy of the estimetes steps from a 30% up to 3%
- Contract value: savings of up to 10% on the value of the contract through the identification of project conflicts
Develop your project with BIM
Write us to know how to carry out your project or your work with the BIM system